Why Give Vitamin D To Children?

Currently, there is much controversy when it comes to supplementing or not supplementing with vitamin D to infants under six months, understanding that breast milk is sufficient food and that its vitamin concentration is very high. However, pediatricians advise giving vitamin D to children from birth.
It is true that our habits have changed and our lifestyle is far removed from when parenting took place in full sunlight. Now, the dangers of ultraviolet light cause children to go outside with more clothing than necessary and covered in sunscreen, so that the sun’s rays do not penetrate their skin and they do not synthesize vitamin D.
What is vitamin D and what is it for?
Vitamins are compounds that our body needs to grow and function normally. Vitamin D is present in all the cells of our body. It is responsible for the absorption of calcium, an essential element for proper bone formation and remodeling.
Vitamin D can be obtained from foods such as egg yolks or liver. We can also acquire it from vitamin supplements or through the skin after exposure to the sun. Our body synthesizes vitamin D naturally, although prolonged exposure to the sun can cause skin cancer or premature aging of the skin.

When we are children, it is a fundamental component, along with calcium, so that we grow up healthy and strong, and it helps us prevent rickets. On the other hand, when we get old, it is essential to avoid bone diseases such as osteoporosis. Therefore, it has several functions, but the most important can be summarized as follows:
- It helps the body in the absorption of calcium present in both food and supplements.
- The muscles use it for their movement.
- The nerves to transmit messages to the brain and to every part of our body.
- The immune system uses it to fight viruses and bacteria.
Symptoms and consequences of vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency does not cause obvious signs, but we can observe certain symptoms that make us suspect that we need an extra contribution, such as fatigue, bone pain or muscle weakness. It is possible that this deficiency is related to an inadequate and unhealthy diet, and may lead to highly serious injuries, such as fractures bones, rickets or loss of bone mass.
Other factors related to its deficit are intestinal absorption problems, lack of exposure to sunlight or a malfunction of the liver and kidneys, these being incapable of transforming vitamin D from the diet into its active principle. In some cases, there seems to be a close relationship with conditions such as diabetes, cancer, or autoimmune diseases such as sclerosis.
Vitamin D supplements to prevent disease
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 42% of children in the world show signs of malnutrition and rickets. Although this is not such a pronounced problem in the first world, it does warn us that newborns have a very low vitamin D concentration.
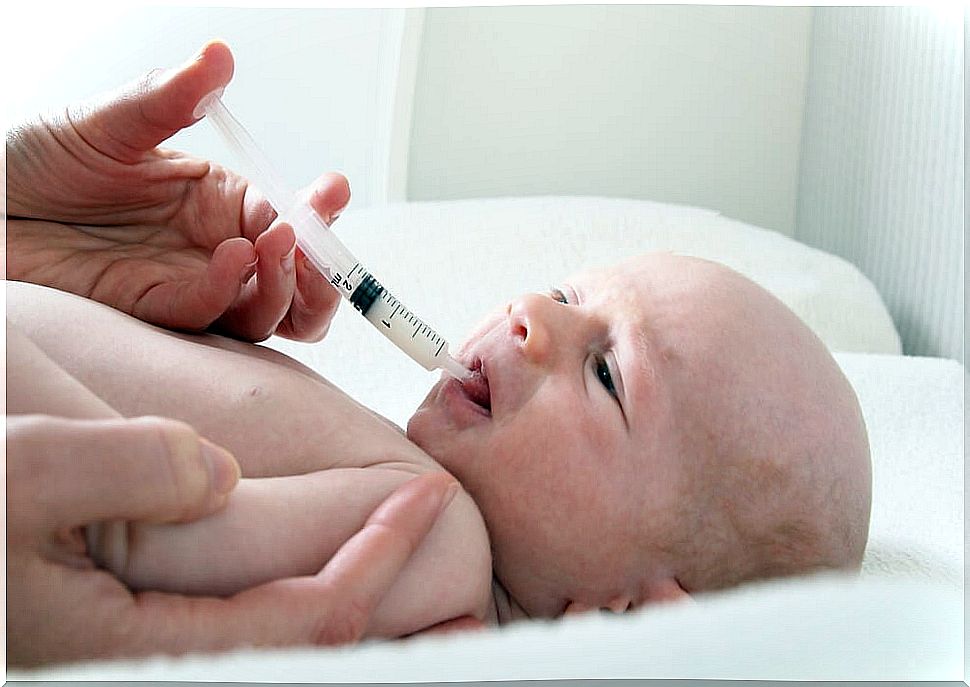
Taking into account the importance of the metabolic functions it performs and the lack of exposure to sunlight, the WHO recommends protecting neonates with an extra supply of vitamin.
The recommended daily amount will depend on age, and it will be the pediatrician who will indicate the most appropriate dose and the time that we must supply it. . Do not lose sight of the fact that an excess of vitamin D can also be harmful.
The Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products warns of the occurrence of severe cases of hypercalcemia in newborns and infants associated with daily administration from cholecalciferol much higher than recommended.
For its part, the American Academy of Pediatrics, while recognizing that the thresholds that determine vitamin D deficiency and the recommended daily intake for children are still the subject of debate, it establishes a recommended daily dose of 400 IU (International Units) shortly after the birth and throughout much of childhood.